Our Inspiration:
In SOBEK®, we derive our strength and energy from our great civilization “The Ancient Egyptian Civilization”, which extends to this day over 7,000 years, which is considered the first civilization the world has ever known. Our historical logo was carefully chosen in line with our field of work, in order to assure our partners and customers around the world that we seek to be an extension of this great history of strength, efficiency, protection, sustainability, and commitment.

SOBEK® (also called Sebek, Coptic: Ⲥⲟⲩⲕ.) was an ancient Egyptian deity with a complex and elastic history and nature. Sobek enjoyed a longstanding presence in the ancient Egyptian pantheon, from the Old Kingdom of Egypt (c. 2686–2181 BCE) through the Roman period (c. 30 BCE–350 CE), more than 5000 Years ago.
He is associated with the Nile crocodile and is represented as a human with a crocodile head. Sobek was also associated with pharaonic power, fertility, and military prowess, He was revered in Egyptian culture, invoked especially for protection against the dangers presented by the Nile and the defender for the people.
In ancient Egypt, the Scarabs Beetle was a widely popular, highly significant symbolic representation of most of the Egyptian gods. Scarabs are amulets and impression seals. Some scarabs were created for political or diplomatic purposes to commemorate or advertise royal achievements. Additionally, scarabs held religious significance and played a role in Egyptian funerary practices.
The ankh or key of life is an ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol used to represent the word for "life" and, by extension, as a symbol of life itself, Early examples of the ankh sign date to the First Dynasty (c. 30th to 29th century BC) by most of the ancient Egyptians pharaohs, and appears as (𓋹) in the Miscellaneous Symbols in the Egyptian Hieroglyphs block.
The “Sun Disk,” held significant religious and symbolic importance in ancient Egyptian culture by the Fifth Dynasty, in the 25th and 24th centuries BC, it represented the sun god Ra, one of the most important deities in the Egyptian pantheon. Ra was considered the creator and sustainer of life, and the sun disk was a powerful symbol of his divine presence and power.

The ankh or key of life is an ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol used to represent the word for “life” and, by extension, as a symbol of life itself, Early examples of the ankh sign date to the First Dynasty (c. 30th to 29th century BC) by most of the ancient Egyptians pharaohs, and appears as (𓋹) in the Miscellaneous Symbols in the Egyptian Hieroglyphs block.
The symbol often appeared in Egyptian art as a physical object representing either life or related life-giving substances such as air or water. Commonly depicted in the hands of ancient Egyptian deities, sometimes being given by them to the pharaoh, it represents their power to sustain life and to revive human souls in the afterlife.

The “Sun Disk,” held significant religious and symbolic importance in ancient Egyptian culture by the Fifth Dynasty, in the 25th and 24th centuries BC, it represented the sun god Ra, one of the most important deities in the Egyptian pantheon. Ra was considered the creator and sustainer of life, and the sun disk was a powerful symbol of his divine presence and power.
The sun disk was often depicted as a circle, sometimes adorned with wings and other symbols. It could be found in many religious texts, temple decorations, and funerary art. The symbol was associated with concepts of light, life, and resurrection. The worship of the sun god and the symbolism of the sun disk persisted throughout ancient Egyptian history, and it remained an integral part of their religious beliefs and artistic expressions.

SOBEK® (also called Sebek, Coptic: Ⲥⲟⲩⲕ.) was an ancient Egyptian deity with a complex and elastic history and nature. Sobek enjoyed a longstanding presence in the ancient Egyptian pantheon, from the Old Kingdom of Egypt (c. 2686–2181 BCE) through the Roman period (c. 30 BCE–350 CE), more than 5000 Years ago.
He is associated with the Nile crocodile and is represented as a human with a crocodile head. Sobek was also associated with pharaonic power, fertility, and military prowess, He was revered in Egyptian culture, invoked especially for protection against the dangers presented by the Nile and the defender for the people.
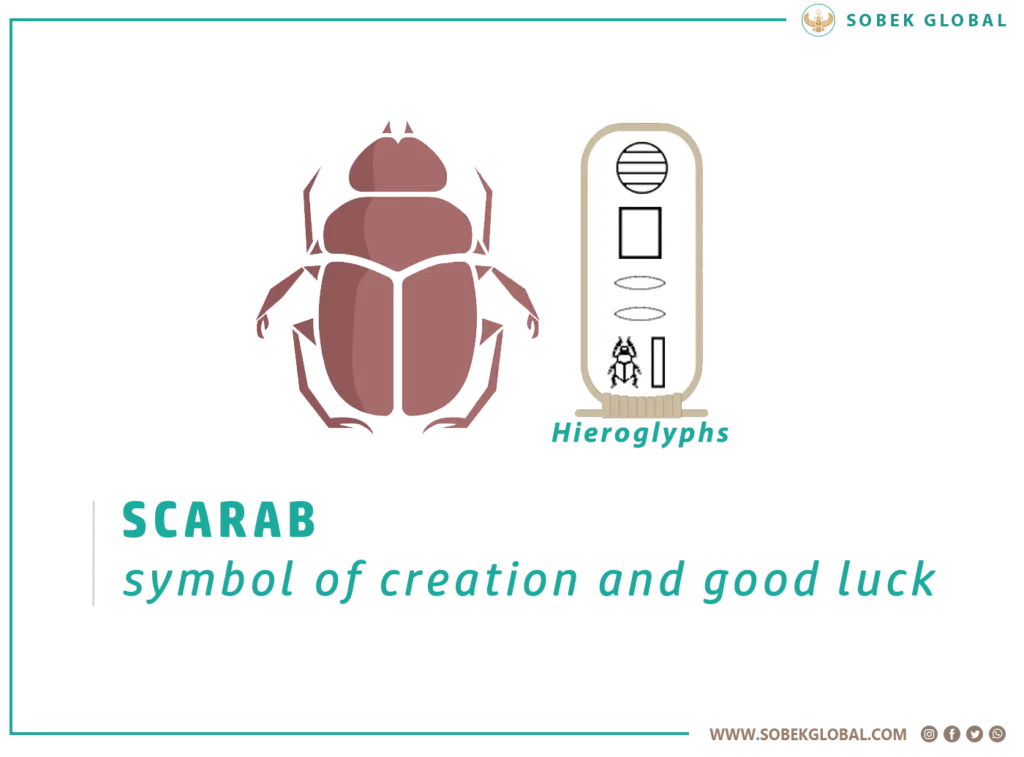
In ancient Egypt, the Scarabs Beetle was a widely popular, highly significant symbolic representation of most of the Egyptian gods. Scarabs are amulets and impression seals. Some scarabs were created for political or diplomatic purposes to commemorate or advertise royal achievements. Additionally, scarabs held religious significance and played a role in Egyptian funerary practices.
Due to their connections to the Egyptian god, amulets in the form of scarab beetles became enormously popular in Ancient Egypt by the early Middle Kingdom (c. 2000 BC) and remained popular for the rest of the pharaonic period and beyond. These artifacts prove to be an important source of information for archaeologists and historians of ancient Egypt, representing important symbols of rebirth and resurrection, prosperity, as well as good luck and fortune.
